Содержание

If you would like a depreciation schedule included in the results so you can print it out, move the slider to the «Yes» position. If you would like the name of the asset, or General Asset Account (GAA), included in the title of the depreciation schedule, enter the name in this field. On the Bakery Accounting other hand, the SYD, or Sum of Years’ Digits method, depreciates more in a product’s earlier lifespan than in its later period.
Impact of salvage value on depreciation calculations

By mastering these adjustments, I can better manage my assets and their depreciation, ensuring that my financial statements reflect the true value of my investments. Our solution has the ability to record transactions, which will be automatically posted into the ERP, automating 70% of your account reconciliation process. Our Financial Close Software is designed to create detailed month-end close plans with specific close tasks that can be assigned to various accounting professionals, reducing the month-end close time by 30%.

How the Double Declining Balance Depreciation Method Works

The double declining balance (DDB) depreciation method is an accounting approach that involves depreciating certain assets at twice the rate outlined under straight-line depreciation. This results in depreciation being the highest in the first year of ownership and declining over time. The Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits Method also falls into the category of accelerated depreciation methods. It involves more complex calculations but is more accurate than the Double Declining Balance Method in representing an asset’s wear and tear pattern. This method balances between the Double Declining Balance and Straight-Line methods and may be preferred for certain assets.
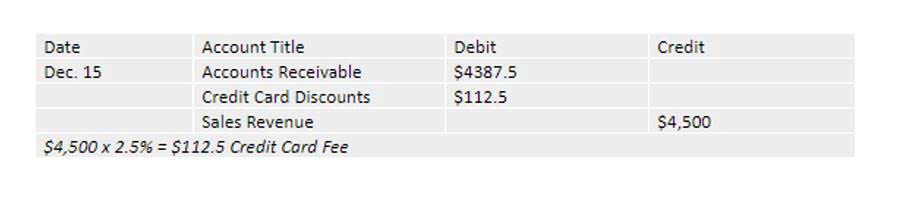
Example 2: Depreciation of Machinery with Variable Lifespan
- Next, divide the annual depreciation expense (from Step 1) by the purchase cost of the asset to find the straight line depreciation rate.
- Understanding the pros and cons of the Double Declining Balance Method is vital for effective financial management and reporting.
- We should have an Ending Net Book Value equal to the Salvage Value of $2,000.
- HighRadius offers a cloud-based Record to Report Software that helps accounting professionals streamline and automate the financial close process for businesses.
The cost of tax preparation varies based on the complexity of your tax return, the experience of the tax professional, and the amount of tax services you seek. Of course, every business is different so in this article we’re diving into what affects tax preparation costs, how to lower those fees, and what to look for in selecting a preparer. In later years, as maintenance becomes more regular, you’ll be writing off less of the value of the asset—while writing off more in the form of maintenance. So your annual write-offs are more payroll stable over time, which makes income easier to predict.
Advantages of Using Double Declining Balance Depreciation

As a result, at the end of the first year, the book value of the machinery would be reduced to $6,000 ($10,000 – $4,000). If the double-declining depreciation rate is 40%, the straight-line rate of depreciation shall be its half, i.e., 20%. Double-declining depreciation charges lesser depreciation in the later years of an asset’s life. In the last year of an asset’s useful life, double declining balance depreciation we make the asset’s net book value equal to its salvage or residual value. This is to ensure that we do not depreciate an asset below the amount we can recover by selling it. For example, if an asset has a useful life of 10 years (i.e., Straight-line rate of 10%), the depreciation rate of 20% would be charged on its carrying value.
- This approach is reasonable when the utility of an asset is being consumed at a more rapid rate during the early part of its useful life.
- Depreciation in the year of disposal if the asset is sold before its final year of useful life is therefore equal to Carrying Value × Depreciation% × Time Factor.
- Each year, you depreciate the asset by a fraction that has the remaining life of the asset as the numerator.
- This formula works for each year you are depreciating an asset, except for the last year of an asset’s useful life.
- In year three, the amount that would be generated by Straight-Line at that point in time would be the depreciable cost, which is now $3,600 divided by three as we only have three years left in the assets life.
- We have helped accounting teams from around the globe with month-end closing, reconciliations, journal entry management, intercompany accounting, and financial reporting.
- It’s a method that can provide significant benefits, especially for assets that depreciate quickly.
- This cycle continues until the book value reaches its estimated salvage value or zero, at which point no further depreciation is recorded.
- So if you have a question about the calculator’s subject, please seek out the help of someone who is an expert in the subject.
- Make sure to check with a tax professional to get this right and make the most of possible tax benefits.
- This gives you the annual depreciation rate if you were using the straight-line method.
- The ending book value for the first year becomes the beginning book value for the second year, and so on.
- The above image doesn’t a much better job of explaining switching depreciation methods than mere words alone.
In the final year, the asset will be further depreciated by $2000, ignoring the rate of depreciation. This is because, unlike the straight-line method, the depreciation expense under the double-declining method is not charged evenly over the asset’s useful life. In the last line of the above depreciation schedule, you will note that the depreciation expense was adjusted downward so as not to depreciate the machine beyond its salvage value.
- Depreciation is an accounting process by which a company allocates an asset’s cost throughout its useful life.
- The table below includes all the built-in Excel depreciation methods included in Excel 365, along with the formula for calculating units-of-production depreciation.
- Our team is ready to learn about your business and guide you to the right solution.
- The first four (cost, salvage, life, and period) are required and the same as used in the DB function.
- Accruing tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid.
- If you’ve taken out a loan or a line of credit, that could mean paying off a larger chunk of the debt earlier—reducing the amount you pay interest on for each period.
Once the rate is established, calculate the depreciation expense for the first year by applying this rate to the asset’s initial book value. In subsequent years, apply the same rate to the asset’s remaining book value, which decreases each year as depreciation is accounted for. This results in a diminishing depreciation expense over time, aligning with the asset’s decreasing utility and value. The book value should not fall below the asset’s salvage value, the estimated residual value at the end of its useful life. If you make estimated quarterly payments, you’re required to predict your income each year. Since the double declining balance method has you writing off a different amount each year, you may find yourself crunching more numbers to get the right amount.
- Egyptian Resurgence 2: The brand new free spins raging rhino no deposit Mummy’s Get back Demo Gamble 100 percent free Slot Game -
- Free hunting treasures deluxe online slot online NZ Pokies Zero Sign up Play Genuine Online game To own Enjoyable -
- Egyptian Revival 2 Demonstration Play Totally free Position sam on the beach slot casino Game -